Uveitis refers to the inflammation that occurs in the uvea, which is composed of the iris, choroid, and ciliary body.
The uvea is a layer located between the outermost sclera and the innermost retina in the eye, containing numerous blood vessels and connective tissues, making it susceptible to inflammation caused by viruses, bacteria, and other factors.
When uveitis occurs, not only the uvea but also the retina and vitreous can be affected. If left untreated for a long time, it can lead to complications such as cataracts, retinal abnormalities, and glaucoma, potentially resulting in blindness. Therefore, timely and appropriate treatment is crucial.
Causes and Symptoms
Uveitis can be classified into infectious uveitis, caused by viruses, bacteria, etc., and non-infectious uveitis, induced by immune responses triggered by surgery, trauma, etc.
Symptoms of uveitis vary depending on its cause and the progression of the condition and may include visual impairment, eye pain, redness, and sensitivity to light.
-
Visual impairment and redness
-
Eye pain and sensitivity to light
Diagnosis
Uveitis can lead to various ophthalmic complications. Therefore, examinations to assess the presence of complications are necessary.
Slit Lamp Examination: It assesses the anterior inflammation, detecting abnormalities in the cornea or iris.
Fluorescein Angiography (FAG): It helps identify retinal vascular inflammation, ischemic areas, neovascularization, etc.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): It provides information on the occurrence of diabetic macular edema, subretinal membranes, etc.
Indocyanine Green Angiography (ICG): It traces inflammatory changes or vascular alterations in the choroid.
Treatment
Uveitis can arise from various causes, and treatment can be tailored based on the identified cause. When the cause is known, it is crucial to undergo regular examinations to check for ophthalmic complications and administer specific treatments for the identified cause. In cases where the cause is unknown, steroid treatment is often effective. However, since this can lead to complications such as hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes, hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol), glaucoma, osteoporosis, cataracts, etc., consultation with a specialist is necessary.
After treatment, preventing the risk of recurrence in uveitis involves avoiding overexertion and stress, reducing alcohol and tobacco use, and ensuring adequate nutrition intake.
-
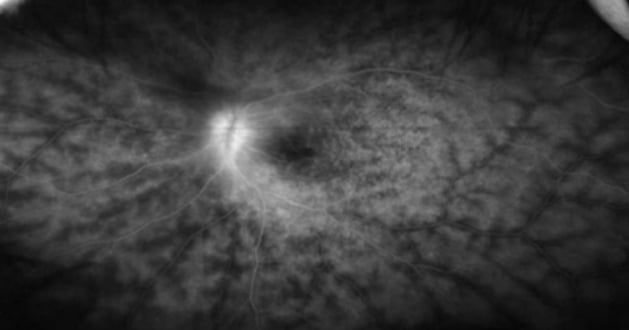
Before Treatment
Leakage of Contrast Medium from Retinal Blood Vessels
- Treatment for the Cause
-
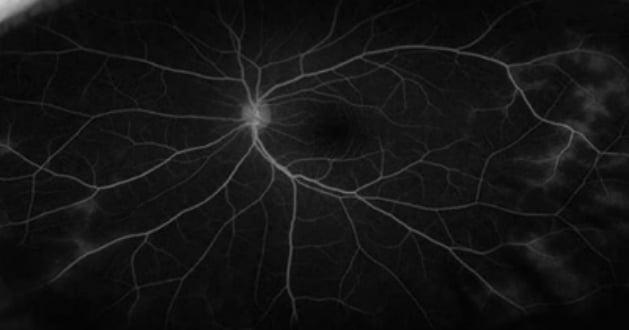
After treatment
Significant Decrease in Leakage of Contrast Medium from Retinal Blood Vessels
The One Seoul Eye Clinic provides the highly effective new drug Humira®,
adalimumab for the treatment of refractory uveitis patients at a much lower cost than general hospitals.
-
Weekdays
08:30 a.m. - 05:30 p.m -
Saturdays
08:30 a.m. - 01:30 p.m -
Lunchtime
01:00 p.m. - 02:00 p.m
8F and 9F Sinsa Square, 652 Gangnam-daero, Gangnam-gu, Seoul
o straight for 5 minutes (330m) on foot from
Exit 6 of Sinsa Station on Subway Line 3
